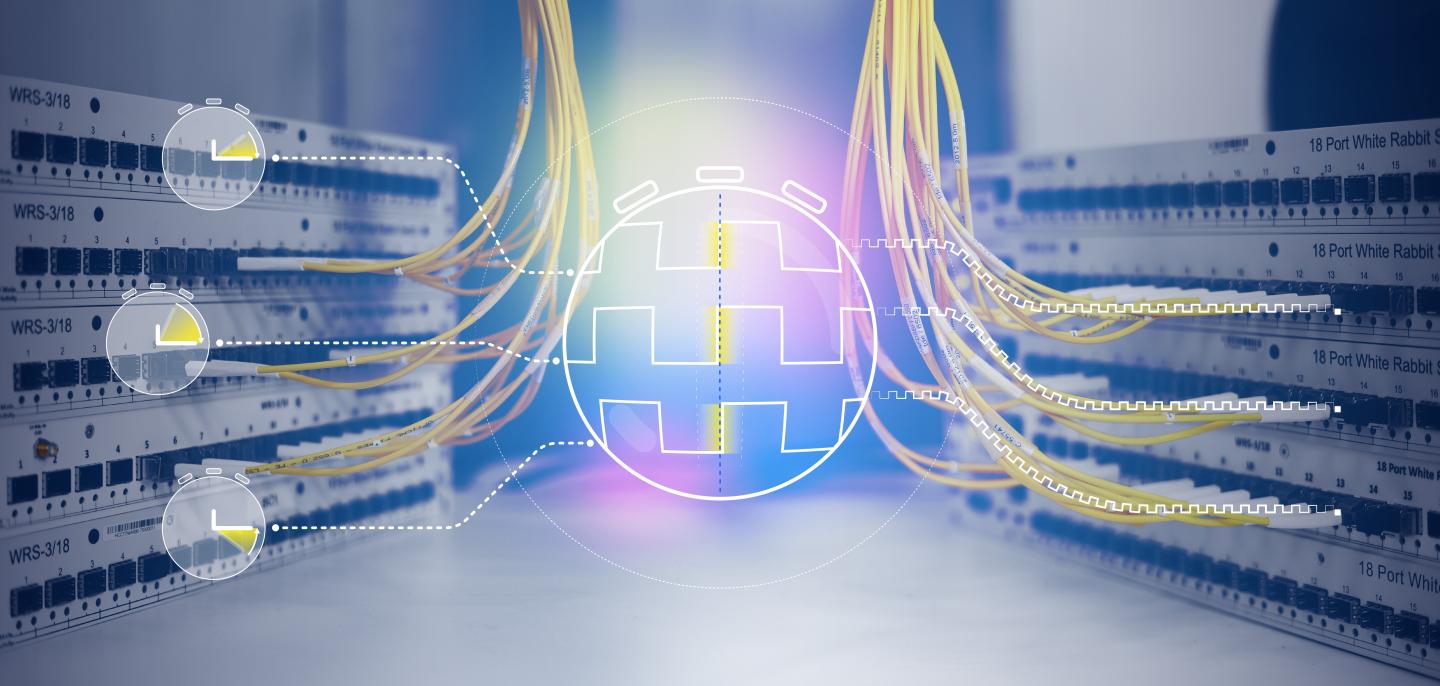
White Rabbit provides sub-nanosecond accuracy and picoseconds precision of synchronization for large distributed systems. It also allows for deterministic and reliable data delivery. White Rabbit allows you to precision time-tag measured data and lets you trigger data taking in large installations while at the same time using the same network to transmit data.
22 March 2024: "CERN launches the White Rabbit Collaboration"
26 June, 2020: "White Rabbit, a CERN-born technology, sets a new global standard".
Advantages & Applications
Advantages
- Based on standards, with the concepts underlying the technology incorporated in the IEEE 1588 standard, under the High Accuracy (HA) profile.
- Open-source allowing you to modify it and adapt it to your needs.
- Able to benefit from a structured global community aims to foster the further uptake of the technology by industry: The White Rabbit Collaboration.
- Already commercially available from multiple vendors.
Applications
- Finance sector (such for example in the Deutsche Borse).
- Large research infrastructure (such as the LHAASO Telescope).
- Data acquisition system of fusion experiments (such as the Swiss Plasma Centre).
- Quantum network experiments (such as NIST paper).
- Tested as a viable alternative to GNSS (JRC report).
Specifications
The White Rabbit Technology allows:
- Sub-nanosecond synchronization
- Ethernet-based gigabit rate reliable data transfer connecting thousands of nodes.
For more details: https://ohwr.org/project/white-rabbit/wikis/home
Developed at
CERN
Licensing
Open Source